In September 2006, six ministries and commissions including the Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) issued the Acquisition of Domestic Enterprises by Foreign Investors Provisions. These permitted an offshore listed company or its shareholder to swap existing or newly issued equity in that company for existing or newly issued equity in a domestic Chinese company.

Partner
Martin Hu & Partners
On 14 January 2009, the State Administration for Industry and Commerce (SAIC) issued the Registration of Capital Contributions Made in the Form of Equity Administrative Measures. Unlike previous local regulations under which only Chinese individuals and enterprises could make capital contributions in the form of equity, these allow non-Chinese individuals, enterprises and other organizations to do so.
Recently, MOFCOM issued the Contribution of Equity in the Establishment of Foreign Investment Enterprises Administrative Measures (Consultation Draft) to regulate the establishment of foreign investment enterprises (FIEs) by domestic and foreign investors with capital contributions in the form of equity interests in enterprises in China.
Participating entities
- Investors, including domestic and offshore natural persons, enterprises and other organizations.
- PRC companies whose equity is to be contributed, including domestic limited liability companies and joint stock limited companies.
- Investee companies, including other domestic limited liability companies and joint stock limited companies (including foreign-invested limited liability and joint stock limited companies, provided that a capital contribution made in the form of equity does not result in cross-shareholding between the investee enterprise and equity enterprise).
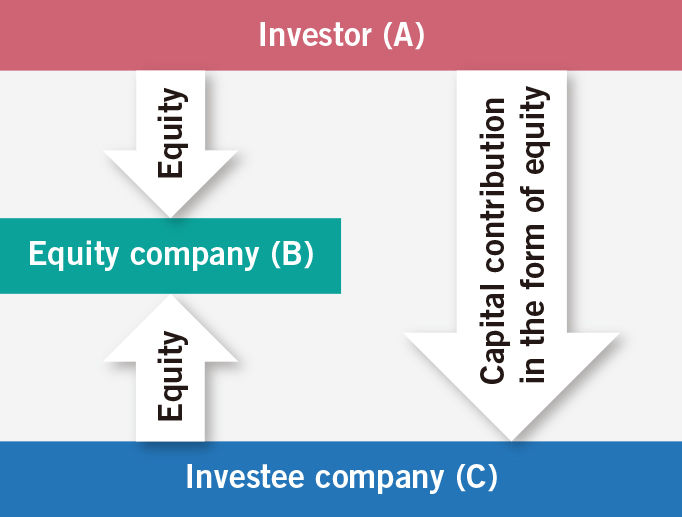
Equity capital contribution model
The investor (A) uses its equity interest in a PRC company (B) (the equity company) as its capital contribution to establish or increase the capital of the investee company (C). Ultimately C becomes a shareholder in B, in place of A. This is illustrated in the above diagram.
Equity contributions and deadlines
Title to the equity used to make a capital contribution should be clear and defect-free, and the equity should be legally transferable. Equity may not be used to make a capital contribution if:
- the equity enterprise’s registered capital has not been paid in full;
- a pledge has been created over the equity;
- the equity has been legally frozen;
- the equity enterprise’s articles of association specify that it may not be transferred;
- a law, administrative regulation or State Council decision specifies that transfer of the equity is subject to approval and no approval has been given; or
- a law, administrative regulation or State Council decision otherwise specifies that it cannot be transferred.
There are two deadlines for capital contributions:
- When an investor makes a capital contribution in the form of equity to a new company, it should be paid in within a year of the company’s establishment. In contrast, under the PRC Company Law, a capital contribution, other than the first instalment, should be paid in full within two years of the establishment of a company.
- Equity used to increase the capital of an enterprise should be paid in before the investee company applies for registration of the change in its registered capital.
Special provisions
In addition to the general provisions mentioned above, the draft Administrative Measures contain the following specific provisions.
- The equity of an FIE that did not participate in or did not pass the previous year’s joint annual inspection of FIEs as well as the equity of a foreign-invested investment company or foreign-invested venture (equity) investment enterprise may not be used as a capital contribution.
- Once a capital contribution has been made in the form of equity, the scope of business of the equity company, the investee company and the enterprises in which the investee company directly or indirectly holds shares are required to comply with the Guiding the Direction of Foreign Investment Provisions, the Foreign Investment Industrial Guidance Catalogue and other foreign investment regulations. An enterprise will be required to divest any non-compliant assets or equity before applying to the make the contribution.
- The price and book value of the equity to be contributed should be determined, based on its valuation, by negotiation between the investor and shareholders in the investee company and others. Any difference between the price and book value of the equity may be credited to the investee company’s capital reserve.
- The provincial level commerce authority where the investee company is located, or MOFCOM, is responsible for approving a capital contribution in the form of equity. If the investee company and the equity company are subject to different approval authorities, the approval authority of the investee company must seek the opinion of the approval authority of the equity company.
Practicalities
Situations involving capital contributions to FIEs in the form of equity are complex and potentially involve different foreign investment laws and regulations.

Senior Associate
Martin Hu & Partners
It will also be necessary to take into account four conditions for determining whether an investor has completed its equity capital contribution obligations set forth in the Supreme People’s Court Several Issues Concerning the Application of the PRC Company Law Provisions (3). These are (1) whether the investor lawfully owns the equity to be contributed and whether such equity can be transferred; (2) whether the equity is free of any rights defects and encumbrances; (3) whether the investor has carried out the equity transfer procedures; and (4) whether the value of the equity to be used as a capital contribution has been appraised.
Kevin Xu is a partner, and Yvonne Lu is a senior associate, at Martin Hu & Partners (MHP Law Firm)

1155 Fangdian Road, Pudong Shanghai, China
Postal code: 201204
Fax: +86 21 5010 1222
www.mhplawyer.com
Martin Hu
Tel: +86 21 5010 1666*966
E-mail: martin.hu@mhplawyer.com
Hansen Zhao
Tel: +86 (21) 5010 1666*977
E-mail: hansen.zhao@mhplawyer.com